We delve into the lore of the lucky horseshoe, tracing its origins and why it remains a popular symbol of good fortune today. For horse owners, we address the frustrating disorder of headshaking in horses, discussing causes, symptoms, and management options. On the farm, we provide a practical guide to checking and maintaining your tractor’s hydraulic system, ensuring efficiency and longevity. Lastly, we help homeowners spot early signs of lawn disease, identifying common issues and their causes to keep your yard healthy year-round. Stay informed and lucky this March!
The Lore of the Lucky Horseshoe
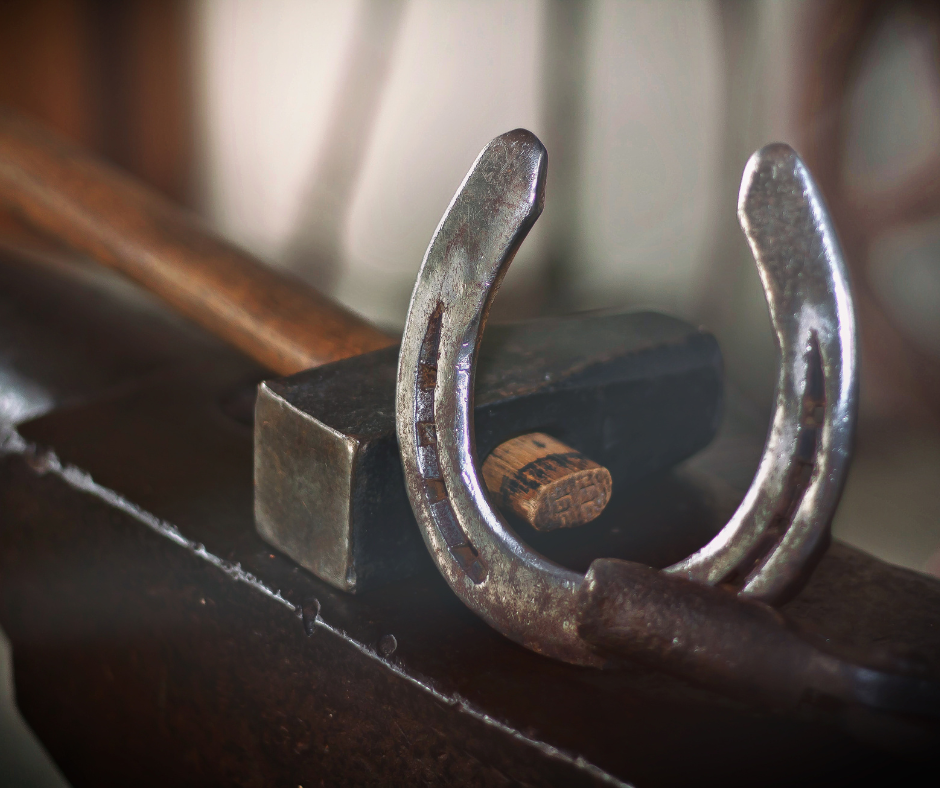

The origin of the lucky horseshoe dates back centuries, rooted in both folklore and practical traditions. Horseshoes, known for their durability, were once used to protect horses’ hooves from wear. They became symbols of protection and good fortune due to their association with horses. As horseshoes were hammered onto horses’ hooves, they were believed to safeguard the animal and its owner from misfortune.
The belief in the horseshoe’s good luck intensified in Europe during the Middle Ages, where it was often hung above doorways to ward off evil spirits. The crescent shape of the horseshoe was key to its symbolic power. Additionally, the iron material of the horseshoe was believed to have protective qualities, especially when it was forged in fire, which was seen as a transformative force.
A common superstition is that the horseshoe should be hung with the open end facing upward, to catch and hold good fortune. In some traditions, the number of nails used in the shoe was also important, with odd numbers being considered especially lucky.
Today, the lucky horseshoe continues to be a popular talisman, often found in homes, businesses, or worn as jewelry. It carries with it a blend of history, charm, and protection that transcends its humble origins as a tool for horses.
P.S. If you are ever in dire need of good luck charm, legend has it that the Holy Grail of lucky horseshoes is one that comes from a gray mare’s hind feet.
Headshaking in Horses: A Frustrating Disorder That Causes Misery

Headshaking in horses is a frustrating and distressing disorder that can significantly affect both the horse and its owner. This condition, characterized by involuntary and repeated jerking or shaking of the head, can occur during riding or while the horse is at rest. While the physical signs are visible and unsettling for riders, the emotional and psychological toll on the horse is often more severe.
The causes of headshaking are varied and can include allergies, neurological disorders, dental issues, or physical discomfort. For many horses, the condition worsens during certain weather conditions, such as in bright sunlight or when the horse is exposed to allergens like pollen. In some cases, the disorder can be linked to issues within the nervous system, such as facial nerve damage or hypersensitivity.
For owners, managing a horse with headshaking can be a challenge. The condition makes riding difficult and often dangerous, as the horse may become unpredictable or uncontrollable. However, the real concern lies in the impact on the horse’s quality of life. The constant discomfort and frustration caused by headshaking can lead to stress, anxiety, and a lack of enjoyment in the horse’s daily activities.
Fortunately, veterinary treatments, including medication, adjustments to tack, and management of environmental factors, can help alleviate symptoms. However, as headshaking is a complex issue, each case requires careful attention to ensure the horse’s comfort and well-being.
How to Check and Maintain the Hydraulics on Your Tractor
Proper hydraulic maintenance is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of your tractor. Hydraulics power many of a tractor’s vital functions, such as lifting, steering, and operating attachments. Here’s the best way to check and maintain the hydraulics on your tractor.

- Check Hydraulic Fluid Levels The first step in maintenance is ensuring that the hydraulic fluid is at the correct level. Check the fluid level with the tractor on a flat surface, and refer to the owner’s manual for the recommended level. Low fluid levels can lead to inefficient operation and potential damage to the hydraulic system.
- Inspect for Leaks Regularly inspect hydraulic hoses and fittings for any signs of wear, cracks, or leaks. Even a small leak can affect performance and lead to a loss of pressure. Replace any damaged hoses or fittings immediately to prevent further issues.
- Replace Hydraulic Fluid and Filter Hydraulic fluid degrades over time, so it’s important to replace it according to the manufacturer’s recommendation. Similarly, replace the hydraulic filter to ensure the fluid remains clean and free from contaminants. This will help prevent premature wear of the pump and other components.
- Check for Air in the System Air in the hydraulic system can cause erratic or jerky operation. If you suspect air is in the system, bleed it out following the manufacturer’s instructions to restore proper function.
- Test the System After performing these checks, start the tractor and test the hydraulic system by operating attachments and functions. Ensure smooth and responsive movement without unusual noises or sluggish performance.
By regularly checking and maintaining your tractor’s hydraulics, you ensure optimal performance and avoid costly repairs. Visit your local dealer for parts or service options!
How to Know if Your Lawn has Disease
A healthy lawn enhances curb appeal, but a sick lawn can quickly ruin its appearance. Recognizing the early signs of lawn disease is crucial for preventing further damage. Regularly inspecting your lawn and understanding common diseases can help you act quickly.

Common Warm-Season Lawn Diseases include Large Patch, which creates circular patches with yellow or orange rings. Leaf Spot appears as dark purple or black spots with a tan center. Pythium Blight shows brown, greasy spots that develop into fungus if untreated. Red Thread creates reddish-pink patches, while Rust manifests as yellow spots that turn orange or red, with powdery spores. Summer Patch leads to dark green or straw-colored patches.
Cool-Season Lawn Diseases include Brown Patch, which causes sunken, tan patches. Pink Snow Mold appears after snow melts, leaving pink or tan patches. Fairy Ring creates dark green patches that may grow mushrooms.
Diseases Affecting Both Grass Types include Dollar Spot, which forms small circular yellow spots on water-soaked grass, and Gray Leaf Spot, marked by gray lesions with purple dots.
Several factors contribute to lawn diseases, including poor watering habits, incorrect mowing height, thick thatch, compacted soil, and high soil pH. Over-watering or under-watering can cause disease, while mowing too short can stress the grass. Thatch buildup invites pathogens, and foot traffic causes soil compaction. Additionally, excessive fertilizer can raise soil pH, making grass more vulnerable.
By identifying these diseases and their causes early, you can maintain a healthy lawn and prevent further damage.








